介绍
Array.sort([compareFunction]) 对Array里面的元素进行升序排序
关于排序的规则
默认的排序
如果compareFunction没有提供的时候,默认把所有Array里面的元素转换为字符串,然后取第一个字符,比较它们的Unicode值,进行正序排序。 这个转为字符串再比较第一个字符的Unicode值,很关键,很多数字的比较,经常就是这样出错的。
[1,2,3].sort(); // ==> [1,2,3] 正确
[9, 80].sort(); // ==> [9, 80] 错误
[9, 80].sort(); // ==> [80, 9] 正确
上面例子中,数组[9, 80]进行sort的时候,先转为为字符串 “9”, “80”, 再比较第一个字符, “9”和”8” 根据这个比较结果进行排序,所以最后80会在9前面,而不是按照它们的数值大小进行排序的。
想自行测试的,可以看看这个demo(http://www.icondownloader.com/demo/sort-stable.html]
compareFunction的排序
进行sort的时候,如果compareFunction提供了,会往compareFunction传两个数组的元素(类似compareFunction(a, b))
取compareFunction的返回值,如果小于0,则表明a小于b;大于0,则a大于b
最后对结果进行升序排序,如果a小于b,则[a, b]; 如果a大于b 则[b, a]
这里有个技巧,在排序的时候,如果想实现降序排序,可以在compareFuction里面实现类似:return !(a-b);
sort stable
关于排序,有个stable的说法,也就是,排序完成之后,对于值相同的元素,在排序结束之后,能否保留其在排序之前的顺序。
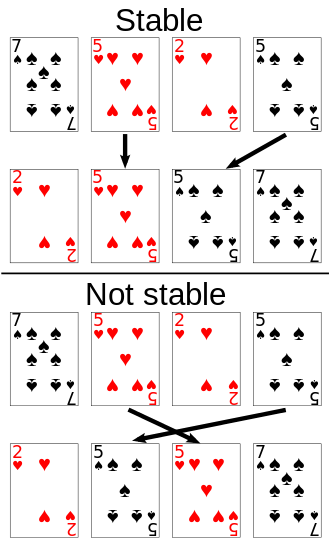
具体的概念可以参考维基百科https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sorting_algorithm#Stability
目前的主流浏览器对stable的sort的支持情况如下:
| Browser | Sort is stable | Sort is unstable |
|---|---|---|
| Firefox 8 | all lengths | |
| Safari 5.1.1 | all lengths | |
| Opera 11.52 | all lengths | |
| Internet Explorer 6, 7, 8 | all lengths | |
| Internet Explorer 9 | all lengths | |
| Android 2.3 Browser | all lengths | |
| Chrome 15 .. 17.0.942.0 | length <= 10 | length > 10 |
可以参考此网站,检测浏览器的sort情况http://ofb.net/~sethml/is-sort-stable.html
sort的效率
可以尝试着对compare function在执行的时候,进行一个计数。这样可以知道每次sort,总共执行了多少次compare function。 我这边写了个demo,有兴趣的可以在自己本机的各个浏览器上测试看看。http://www.icondownloader.com/demo/sort-compare-function-call-times.html 这边我贴出我自己Mac OSX Yosemite 10.10.4下的浏览器的运行结果
## chrome 版本 42.0.2311.135 (64-bit)
Array length is: 5 and sort call compare 7 times;
Array length is: 10 and sort call compare 23 times;
Array length is: 11 and sort call compare 22 times;
Array length is: 12 and sort call compare 19 times;
Array length is: 13 and sort call compare 27 times;
Array length is: 14 and sort call compare 25 times;
Array length is: 15 and sort call compare 24 times;
Array length is: 20 and sort call compare 29 times;
Array length is: 50 and sort call compare 80 times;
Array length is: 100 and sort call compare 206 times;
Array length is: 1000 and sort call compare 1996 times;
Array length is: 10000 and sort call compare 20206 times;
## Safari 版本 8.0.7 (10600.7.7)
Array length is: 5 and sort call compare 8 times;
Array length is: 10 and sort call compare 23 times;
Array length is: 11 and sort call compare 28 times;
Array length is: 12 and sort call compare 31 times;
Array length is: 13 and sort call compare 35 times;
Array length is: 14 and sort call compare 40 times;
Array length is: 15 and sort call compare 44 times;
Array length is: 20 and sort call compare 65 times;
Array length is: 50 and sort call compare 232 times;
Array length is: 100 and sort call compare 568 times;
Array length is: 1000 and sort call compare 8996 times;
Array length is: 10000 and sort call compare 123583 times;
## Firefox (Developer Edition) 40.0a2 (2015-05-29)
Array length is: 5 and sort call compare 6 times;
Array length is: 10 and sort call compare 26 times;
Array length is: 11 and sort call compare 24 times;
Array length is: 12 and sort call compare 33 times;
Array length is: 13 and sort call compare 48 times;
Array length is: 14 and sort call compare 48 times;
Array length is: 15 and sort call compare 37 times;
Array length is: 20 and sort call compare 70 times;
Array length is: 50 and sort call compare 245 times;
Array length is: 100 and sort call compare 574 times;
Array length is: 1000 and sort call compare 8600 times;
Array length is: 10000 and sort call compare 114046 times;
从上面的数据可以看出两个结论:
chrome的执行效率明显高于Safari和Firefox。但是chrome的sort是unstable的,而Safari和Firefox是stable的。是不是可以认为,因为chrome不需要考虑stable,所以提高了执行效率。
可以看出随着数组长度的增加,比较的次数是指数增加的
用map来提高提高sort的性能
从上面的结论2可以知道,在数组长度很长的时候,compareFunction的调用次数是很多的,这个时候,提高compareFunction的效率就很有必要性了。 现在咱们构建一个数组
var arr = \[\],
arrLen = 1000,
i = 0;
function makeWord(){
var word = \[\],
words = \['A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z','a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k','l','m','n','o','p','q','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z'\],
wordsLength = words.length,
arrMinLen = 3,
arrLen = arrMinLen + Math.floor( Math.random()*9 ),
i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < arrLen; i++){
word.push( words\[Math.floor( Math.random()*wordsLength )\] );
}
return word.join('');
}
for (i = 0; i < arrLen; i++) {
arr.push( makeWord() );
}
然后比较一下它们小写字母状态下的排序
// 未优化
arr.sort(function(a, b){
return +(a.toLowerCase() > b.toLowerCase()) || +(a.toLowerCase() === b.toLowerCase())-1;
});
// 优化后
// 用一个临时数组来保存位置和计算后的数值
var mapped = list.map(function(el, i) {
return { index: i, value: el.toLowerCase() };
})
// 排序这个已经计算后的临时数组
mapped.sort(function(a, b) {
return +(a.value > b.value) || +(a.value === b.value) - 1;
});
// 根据位置信息 对应映射生成一个排序后的数组
var result = mapped.map(function(el){
return list\[el.index\];
});
// 不支持map的时候的兼容方法
var tmpArr = \[\],
result = \[\],
i = 0,
len = arr.length;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tmpArr\[i\] = {index: i, value: arr\[i\].toLowerCase()};
}
tmpArr.sort(function(a, b) {
return +(a.value > b.value) || +(a.value === b.value) - 1;
});
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
result\[i\] = arr\[tmpArr\[i\].index\];
}
具体的执行效果可以看看jsperf里面的这个地址http://jsperf.com/arraysortperform
参考文章:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/sort
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Grammar_and_types#Unicode
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Lexical_grammar#String_literals
http://ofb.net/~sethml/is-sort-stable.html
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3026281/array-sort-sorting-stability-in-different-browsers

